
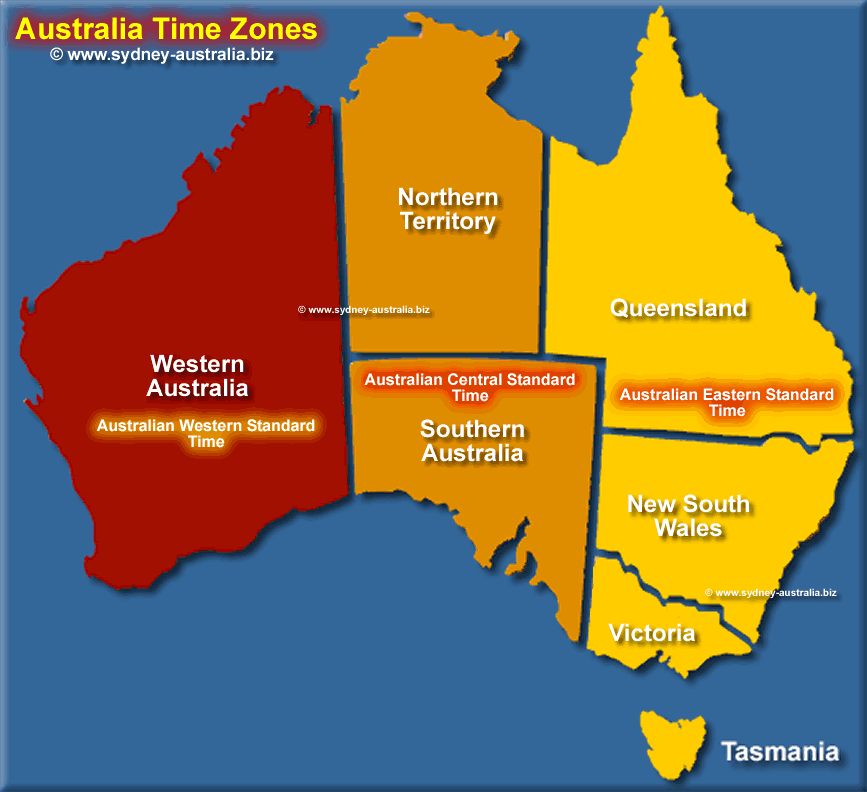
This is part of the Nullarbor Plain, a vast, dry, flat, expanse of scrubland and not much else besides nature. The northern boundary is less precise but it doesn’t really matter. A highway sign reminds travelers to account for this peculiarity.ĪCWST is observed only in a tiny sliver in the far southeastern corner of Western Australia along the Eyre Highway, extending from just outside of Caiguna to Border Village, about 50 metres across the state line into South Australia, for a total length of about 340 kilometres. Visitors entering or leaving ACWST have to remember to set their watches in the proper direction either forward or back by 45 minutes. This is quite rare, something found nowhere else except Nepal and in a few small, isolated corners of the globe. Yes, a time zone that’s based not on the hour or the half-hour, but on the quarter hour! With Western Time at UTC+8:00 and Central Time at UTC+9:30, splitting the difference makes the so-called Central Western Time UTC+8:45. However Australia also has an unofficial but de facto hybrid time zone called “Australian Central Western Standard Time” (ACWST), which is set halfway between the official Western and Central times. Overall, Australian time is fairly straightforward and understandable. Far-flung Australian island territories and its Antarctic stations add a few more complexities. Individual Australian states and territories determine whether to recognise Daylight Saving Time (DST) or not. It’s pretty simple to understand even bearing in mind that Australian Central Standard Time aligns with the half-hour (UTC+9:30). View Australia Daylight Saving Time for more details and a schedule of start and end dates.Continental Australia is divided into three standard time zones, Western, Central and Eastern. Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST) becomes Australian Eastern Daylight Time (AEDT), and so forth.
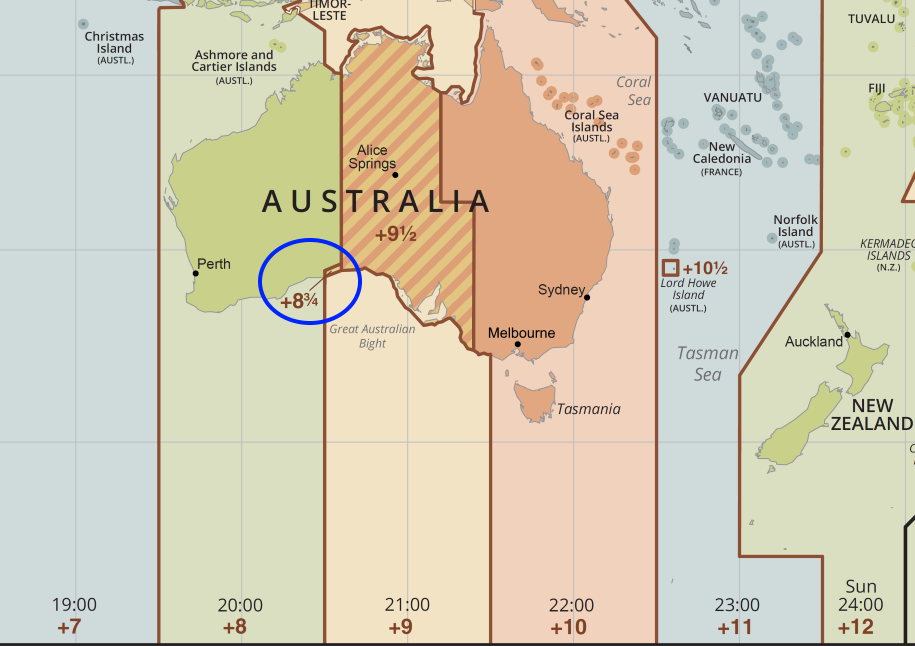
The names in each time zone change along with Daylight Saving Time. As an example Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST) which is UTC/GMT+10 is set ahead to UTC/GMT+11 and is then referred to as Australian Eastern Daylight Time (AEDT). During periods of Daylight Saving Time clocks are advanced by one hour. The Australian Capital Territory, New South Wales, South Australia, Tasmania and Victoria all start and end daylight saving time on the same dates. (UTC/GMT +10:00) Australian Eastern Time Zone. (UTC/GMT +9:30) Australian Central Time Zone. (UTC/GMT +8:45) Central Western Time Zone. (UTC/GMT +8 ) Australian Western Time Zone, Casey Time Zone. (UTC/GMT +7) Davis Time Zone and Christmas Island Time Zone. (UTC/GMT + 6:30) Cocos Islands Time Zone. (UTC/GMT +5) Mawson Station Time Zone and Heard and McDonald Islands Time Zone. Broken Hill observes Australian Central Standard Time (ACST) which is UTC/GMT + 9 1/2 and Lord Howe Island observes UTC/GMT + 10 1/2.Ī total of nine distinct time zones are used by Australia and their external territories. Most of Australia uses three standard time zones, Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST) which is UTC/GMT+10, Australian Central Standard Time (ACST) which is UTC/GMT + 9 1/2 and Australian Western Time (AWST) which is UTC/GMT +8.Īlthough most of New South Wales observes Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST), which is UTC/GMT+10, the two communities of Broken Hill and Lord Howe Island are exceptions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
